Overview
Incentive, which is represented as carrots and sticks, gives human motivation to do something. Why do we need to consider incentive issues in designing information systems? If an information system is implemented, users may use the system in a different way from the expectation of the system designer. In the worst case, any users will not try to use the system. To avoid such failures, we need to design incentives in an appropriate way.
To realize the users’ participation and retention, machines (computers) need to understand what incentives affect human behaviors. More than one incentives are available. Thus, we have to find the best incentive-mix. This research field is called mechanism design and has been actively studied as an interdisciplinary field including economics (game theory) and computer science. The information economics group in Ishida-Matsubara laboratory tries to identify the structures of participative motivation for non-monetary incentive as well as the monetary incentive and develop a method to apply the obtained lessons to various fields such as voting systems and profit distribution for the composite services.
Research
Costly Voting with Sequential Participation
This paper examines the property of the m votes to win mechanism. Voting is an effective way to make a collective decision but voting behaviors, e.g., monitoring the voting process, may incur a cost, that is, voting is often costly. In this case, compulsory voting incurs a larger cost. Random decision making can reduce the cost for voting but is skeptical in the quality of decision making. That is, we face the problem of how to balance the quality of collective decision making with the reduction of the cost for voting. To solve this problem, this paper focuses on the m votes to win mechanism, in which voters sequentially vote and if an alternative receives m votes; the voting process immediately terminates, and the alternative received m-votes wins. The similar voting mechanism is actually used in the Apache projects. However, the property of the m votes to win mechanism has not sufficiently studied. The questions include how to find a desirable value of m and what situation this mechanism is superior to other mechanisms. To answer these question, we create the discussion model where two alternatives are included and analyze what voting strategy is rational. Based on the analysis, we examine what factors affects the social surplus. That is, we examine to what extent the quality of collective decision making and the reduction of the cost for voting are well balanced, and clarify whether the m-votes to win mechanism is superior to the compulsory voting or the random decision making regarding social surplus.
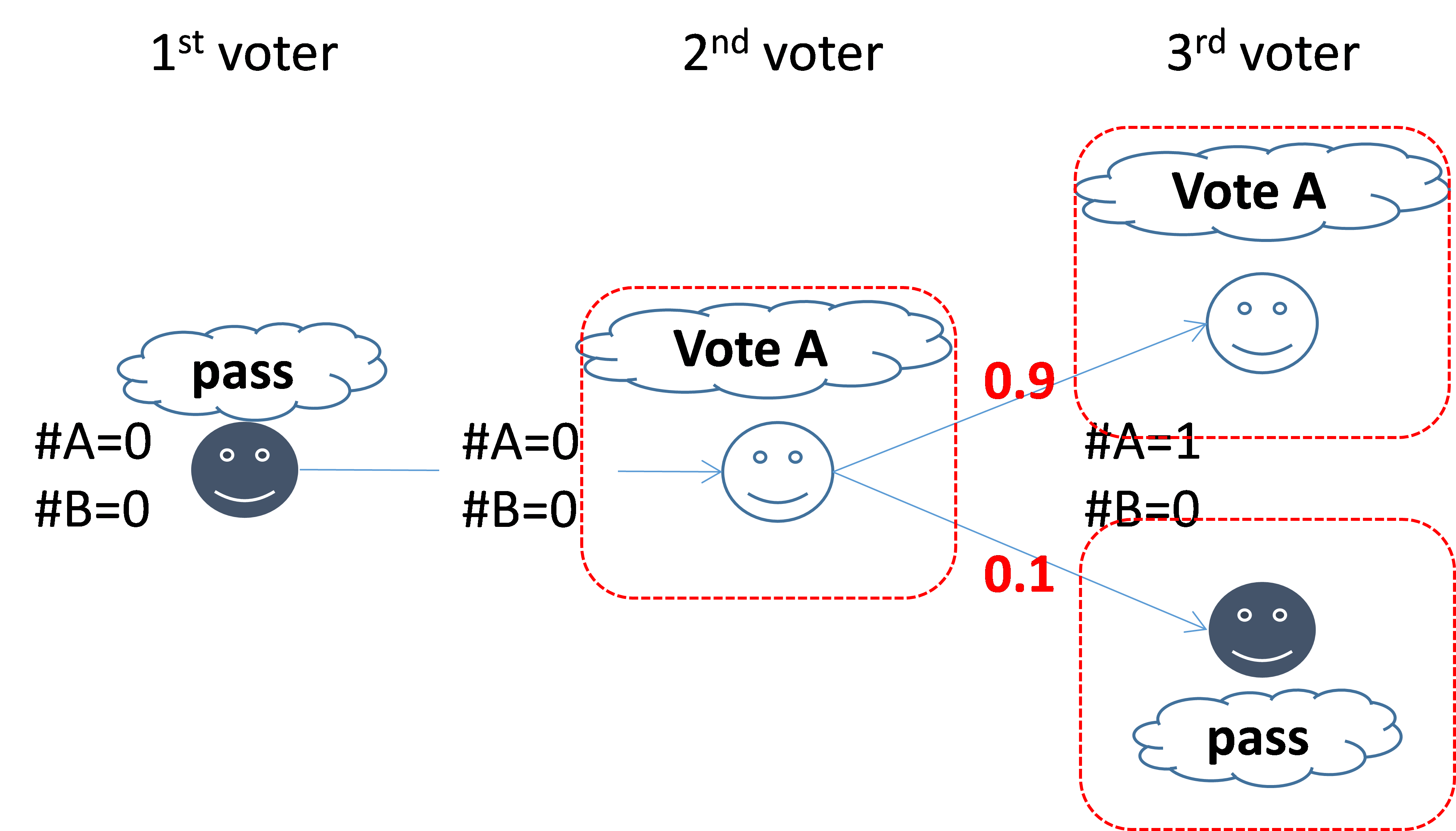
- Ryuya Kagifuku and Shigeo Matsubara: Costly Voting with Sequential Participation. The 14th International Conference on Principles and Practice of Multi-Agent Systems (PRIMA-2011), pp. 68-82, Wollongong, Australia, 2011
Profit Sharing in Service Composition
Component services are often provided by different organizations, which needs to determine how to divide the profit obtained for the composite service to the component service providers. Previous studies have mainly focused on the process of aggregating multiple component services into a composite service. However, the process of the profit sharing has not yet discussed sufficiently. This problem can be formalized as a coalition game in the game theory. However, its flexibility of defining the policy of utilizing the services causes a problem. This paper shows that the existing profit sharing methods, more precisely, neither the equal division method nor the division method based on the Shapley value cannot satisfy the following two desiderata; (1) the sufficient level of service provision is attained, and (2) component services are not broken up more than is necessary. Moreover, we examine what factors make difficult to achieve the sufficient level of service provision, and give a discussion toward mitigating this problem.
Shigeo Matsubara: Profit Sharing in Service Composition. 9th International Conference on Service Oriented Computing (ICSOC2011), pp. 645-652, Paphos, Cyprus, 2011.
- Shigeo Matsubara: Profit Sharing in Service Composition. 9th International Conference on Service Oriented Computing (ICSOC2011), pp. 645-652, Paphos, Cyprus, 2011.
